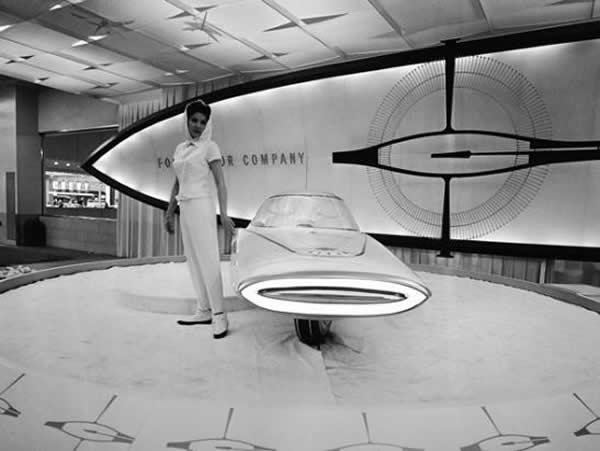
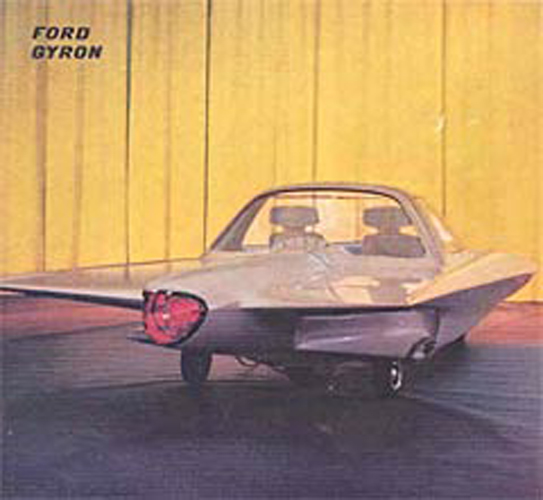
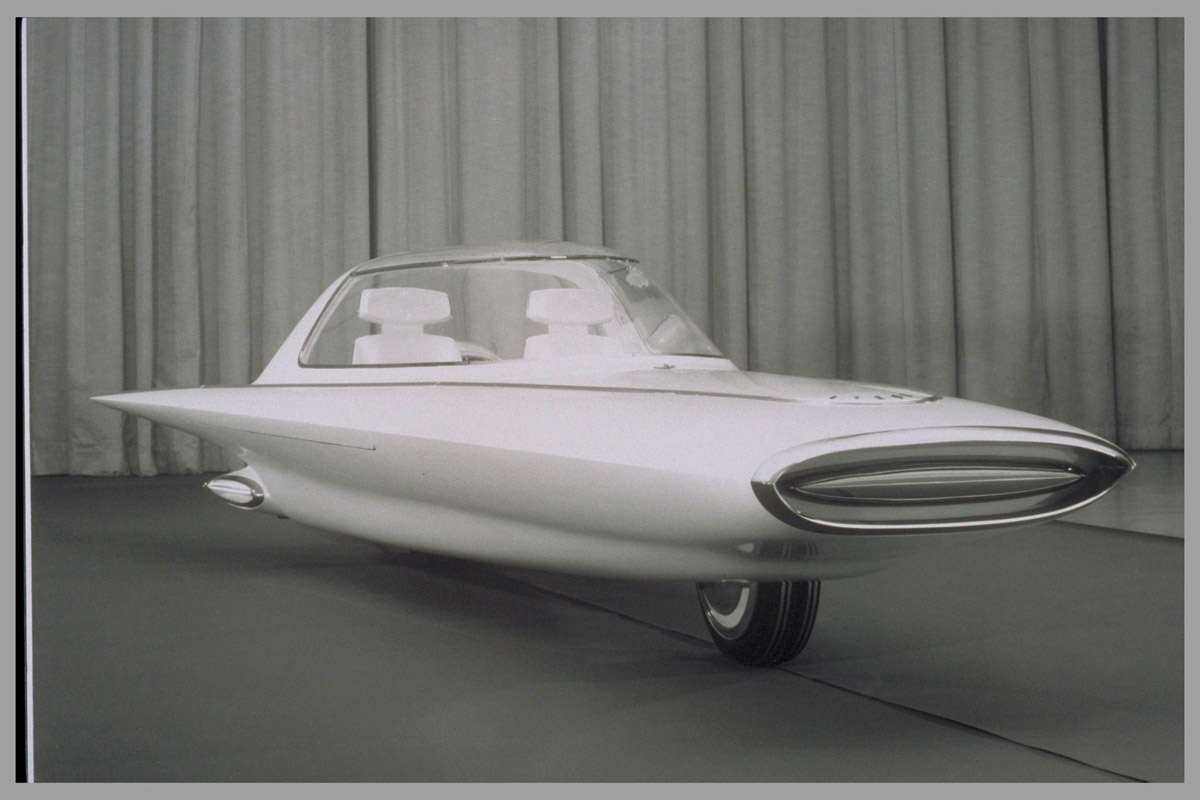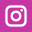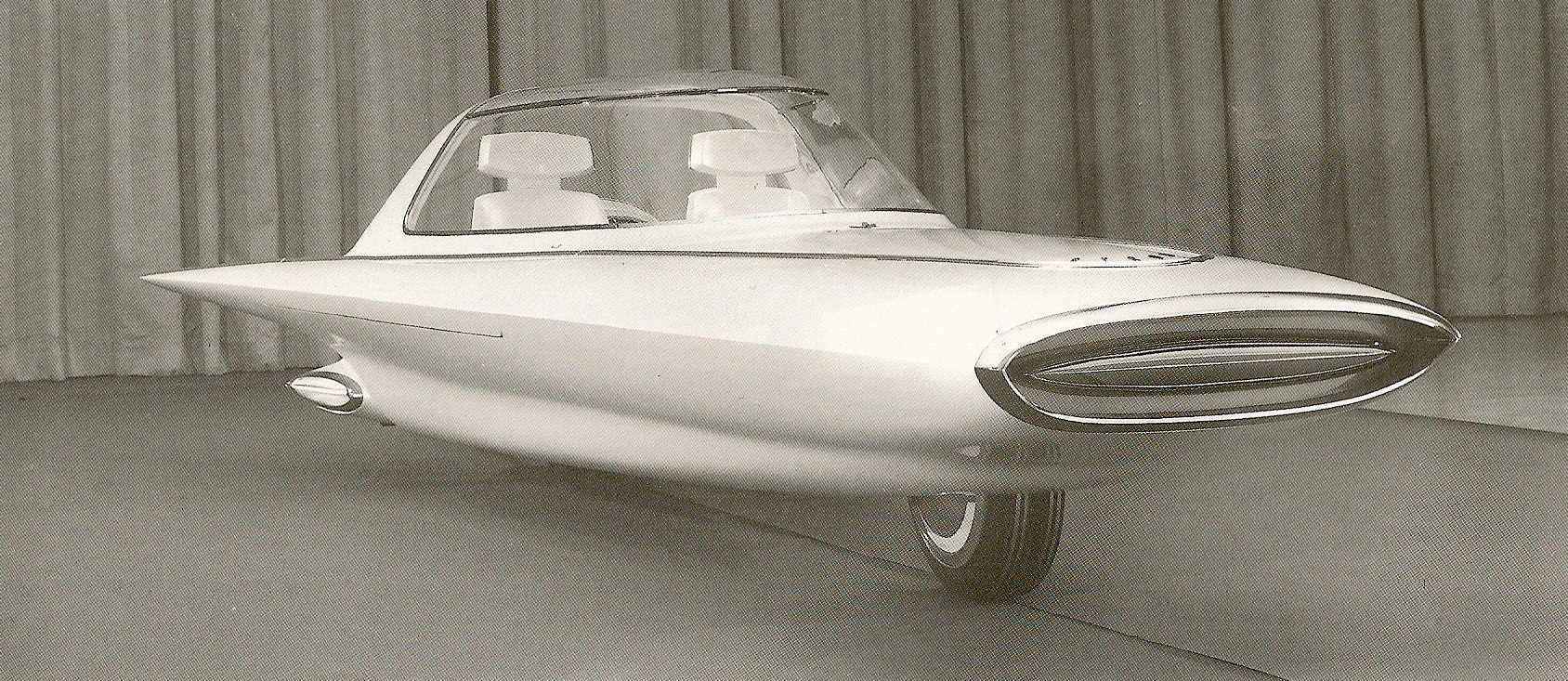

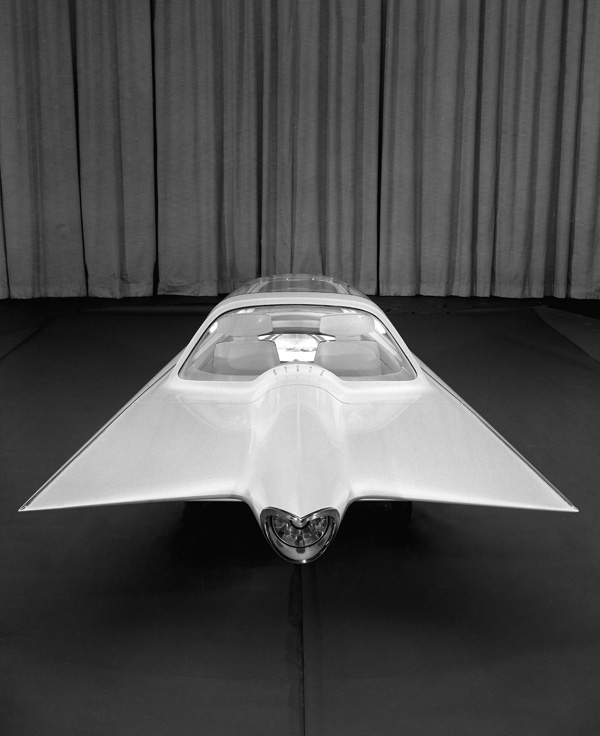





A gyroscopically controlled two-wheeled car called the Gyron.
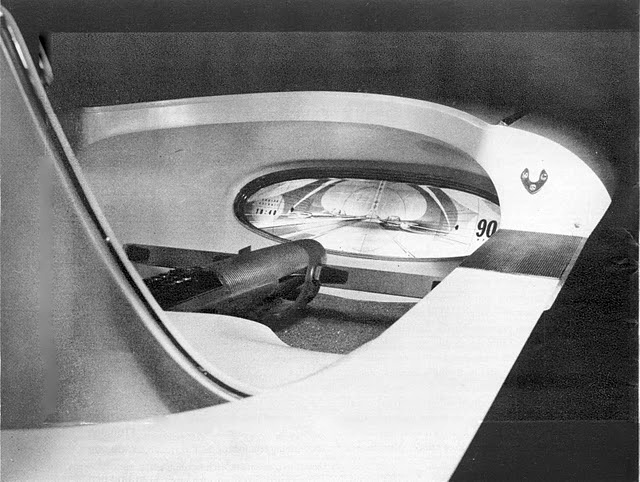
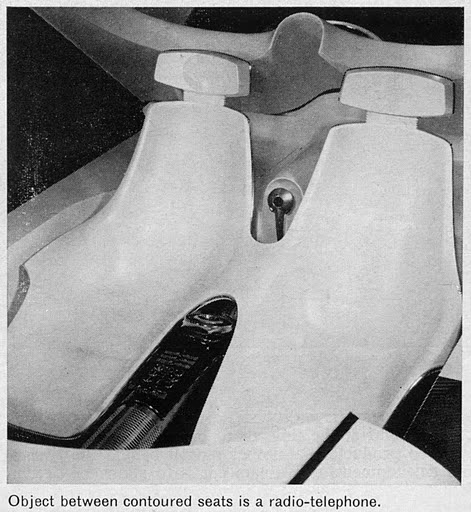
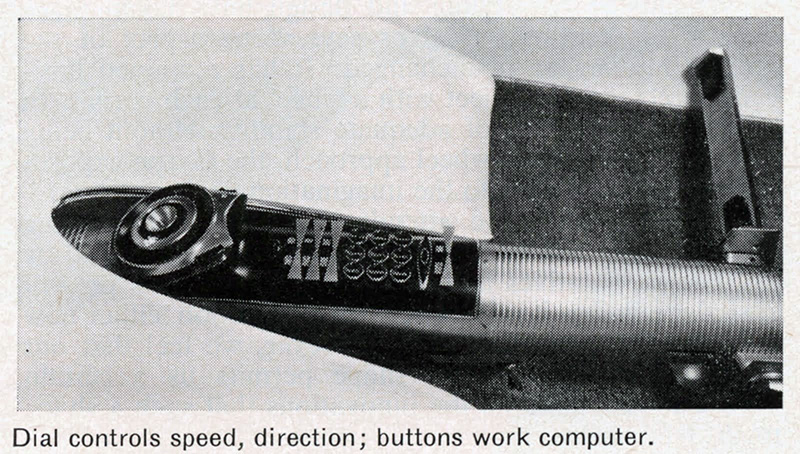
The two-wheeled Gyron, however, would shortly afterward consume much of Tremulis’s effort and time. As the Farrells wrote, Tremulis – whose chief and overwhelming concern was for aerodynamics – believed his design for a two-wheeled gyroscopically balanced car would represent the ultimate in automotive aerodynamics. “In short, Tremulis expected the Gyron to be a genuine breakthrough that would influence all future car design.”The earliest Gyron sketches were rendered in 1956, but Tremulis renewed his interest in the Gyron after learning of GM’s 1959 Firebird III concept, which was hailed as the world’s most advanced and most exotic car. Tremulis felt he could do better. At about that time, Tremulis’s superiors at Ford assigned new hire Syd Mead to work with Tremulis on the Gyron, and together they convinced Ford to let them build a full-scale version of the car. Because a gyroscope of sufficient size to keep the full-scale Gyron upright proved far too expensive for the show car, a pair of wheels on outriggers were added to the design to keep the Gyron upright on the show stand (copywriters explained them away as necessary at low speeds and noted they’d retract at higher speeds); however, its front wheel did steer via a console-mounted dial, and an electric motor did propel the fiberglass-bodied show car up to about 5 MPH. The Gyron debuted in 1961 and would be one of Tremulis’s last projects at Ford, though he would continue to pursue the idea of a two-wheeled gyro car long after he left the company. The fire that destroyed Ford’s Rotunda reportedly took the Gyron as well.Daniel Strohl – blog.hemmings.com